Describe the Flow of Energy in the Kelp Forest Ecosystem
There are about 30 different species of kelp worldwide. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.

Marine Food Chain Kidspressmagazine Com Food Chain Diagram Ocean Food Chain Food Chain
Kelp are large brown algae that live in cool relatively shallow waters close to the shore.

. Small fishes eat th. Groupsspecies that are the same across both ecosystems are in bold and those omitted from either the pre-or post-invasion systems were not recorded in the surveys carried out by Field et al. Functional groups and important species used in the pre-and post-invasion ecosystem models of the Bettys Bay kelp forest.
1980 and Blamey et al. Ecosystems depend on a constant flow of energy and the recycling of materials. The energy flow in the ecosystem is important to maintain an ecological balance.
The energy captured by autotrophs does not go back to the sun the energy that passes from autotrophs to herbivores does not revert back and as it moves progressively through the various trophic levels it is no longer available to the. High energy storms or swells can uproot entire plants and break away fronds. Kelp forests are iconic nearshore ecosystems characterized by expansive swathes of fast-growing brown algae in the order Laminariales.
Kelp forests are home to many species including the New Zealand sea lion. Kelp are large brown algae Phaeophyta that live in cool relatively shallow waters close to the shore. Characterized by severe storms and warm water El Niño Southern Oscillation Events often devastate kelp forests.
They grow in dense groupings much like a forest on land and are found predominantly along the Pacific coast from Alaska to parts of Baja California. The uppermost layer of the kelp forest is. Explain the importance of producers in an ecosystem.
Organisms in an ecosystem acquire energy in a variety of ways which is transferred between trophic levels as the energy flows from the base to the top of the food web with energy being lost at each transfer. Many fish species use kelp forests as nurseries for their young while seabirds and marine mammals like sea lions sea otters and even gray whales use them as shelter from predators and storms. Decomposers in a kelp forest ecosystem Autotroph who creates their own food via photosynthesis and chemosynthesis Definition of Producer Heterotroph who consumes other organisms for energy Definition of Consumer Heterotroph that get their energy from consuming decomposing matter and converting it to its elemental state Definition of Decomposer.
Since the energy gets used up throughout the entire cycle of flowing through the ecosystem it cannot be recycled. The forest layers help describe this complex ecosystem. These underwater towers of kelp provide food and shelter for thousands of fish invertebrates and marine mammal species.
Kelp bass- These fish feed on small invertebrates hidden among the kelp fronds. Use the energy pyramid to answer the following questions. Animals and plants are interdependent.
Kelp forests comprise one the oceans most diverse ecosystems. They grow in dense groupings much like a forest on land. They can be divided into layers including the canopy understory and forest floor.
Firstly there is one way along which energy moves ie. Changes in food web structure and energy flow in kelp forest ecosystems on the south-west coast of South Africa following the. Around the kelp forest to find food.
Sea urchins can destroy entire kelp forests at a rate of 30 feet 9 m per month. Sea sponge- Sponges filter tiny food particles and bacteria out of the water that flows through them. Energy comes in the ecosystem from outside source ie.
Bull kelp a species of large seaweed forms thick kelp forests along the coast of New Zealand. Kelp forests are highly productive coastal habitats that serve as biodiversity hotspots and provide valuable ecosystem services. You can see kelp forests in many of.
Ecosystem of sallow water is oceans Driven by sunlight and photosynthesis Primary producers are Kelp and algae. Ecosystems exist underground on land at sea and in the air. Baseline models that were developed to describe the shift in ecosystem state reflected an increase in the presence of kelp sessile species and lobsters and the decline of encrusting algae and herbivores.
Plants and animals interact in feeding relationships called food chains. Ecosystems that support many interconnected food webs. The organisms use part of this energy part of it is lost as heat and part.
How would the populations of other organisms in the energy pyramid be affected if the population of sea urchins suddenly decreased. Notably while the role of kelp as habitat-forming or foundation species is well-documented a. A part of the energy is stored within the plants.
The audio illustrations photos and videos are credited beneath the media asset except for promotional images which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. All others should have been completed last night for HW. A school of French grunts.
Identify and describe the 4 types of consumers. What effect the event will have on the flow of energy through the kelp forest ecosystem Part C. They need a deeper water to breed and the juveniles settle among the blades of the kelp.
Energy flows through the ecosystem through different levels starting with the process of photosynthesis. Unidirectional flow of energy. Despite being one the largest marine biomes kelp forests have been drastically understudied relative to other marine systems.
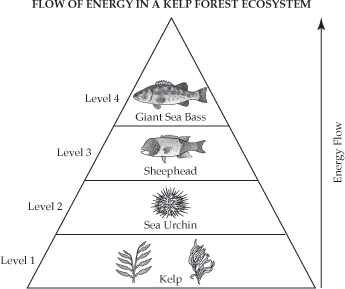
Construct an Energy Pyramid An energy pyramid is a diagram of the amount of the suns energy that is stored in each level of organisms in a food web. Expert-verified answer 1 priyankatutor In the kelp forest Carbon move from photosynthetic plant to other consumers. While in Hydrothermal vents carbon moves from bacteria to other consumer.
Ese habitats are found along Characterizing energy flo w in. The queen conch and the manatee grass. They provide a variety of habitats for animals at all trophic levels.
The producers synthesise food by the process of photosynthesis. Complete Practice Problems Set 1. Food Chains in the Kelp Forest.
The process ends when the carnivores die and get decomposed thereby becoming food for plants and starting the cycle again. Edited by Laurie Dumdie Wendy Naruo and Pat Rutowski. The remaining energy is utilised by the plants in their growth and development.
This was assigned yesterday and you are just to complete Free Response 2 and 4 and MC 1 and 2. They progress through seasonal cycles. Up to 24 cash back The energy pyramid below shows the flow of energy through the organisms in a kelp forest ecosystem in the Pacific Ocean.
These sea lions hunt octopus and squid that. The turtle grass the sand and the cushion sea stars. Kelp forests harbor a greater variety and higher diversity of plants and.

Kelp Forest Ecosystem Need Diagonal Kelp Rocks With Urchins And Sea Stars Marine Ecosystem Ecosystems Kelp Forest

Bing Wallpapers Page 1 Kelp Forest San Clemente Island Scenery Pictures

Expert Verified Just As Energy Flows Through An Ecosystem Matter Also Moves From Organism To Brainly Com

How Does Energy Flow And Is Transferred Through An Ecosystem Ppt Download

3 Ocean Ecosystems Kelp Forests Sargasso Sea Seagrass Meadows Dummies
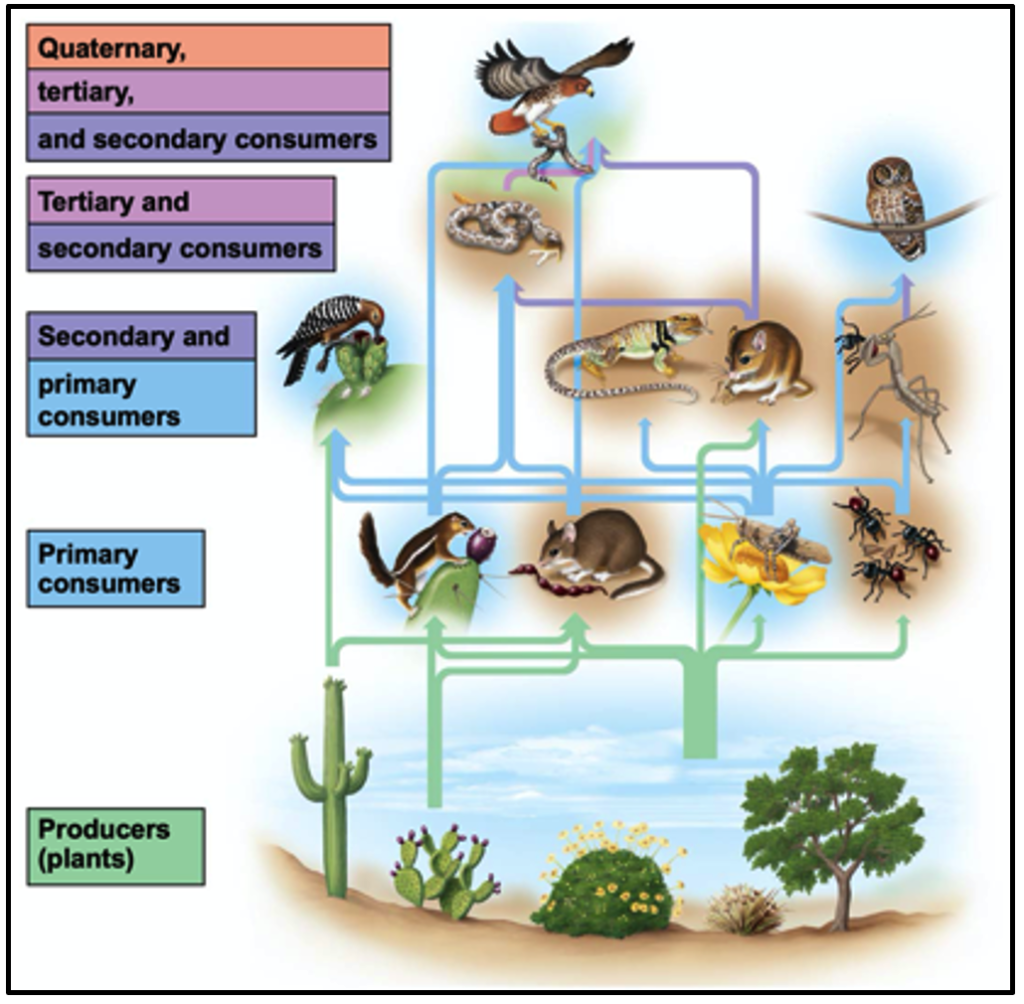
Trophic Interactions In The Kelp Forest Professor St John S Instructional Materials

Food Chain Kelp Forests Kelp Forest Food Webs Projects Ocean Food Web

Food Chains Food Webs The Mesoamerican Coral Reef Coral Reef Food Web Coral Reef Food Web

The Kelp Forest Food Web Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
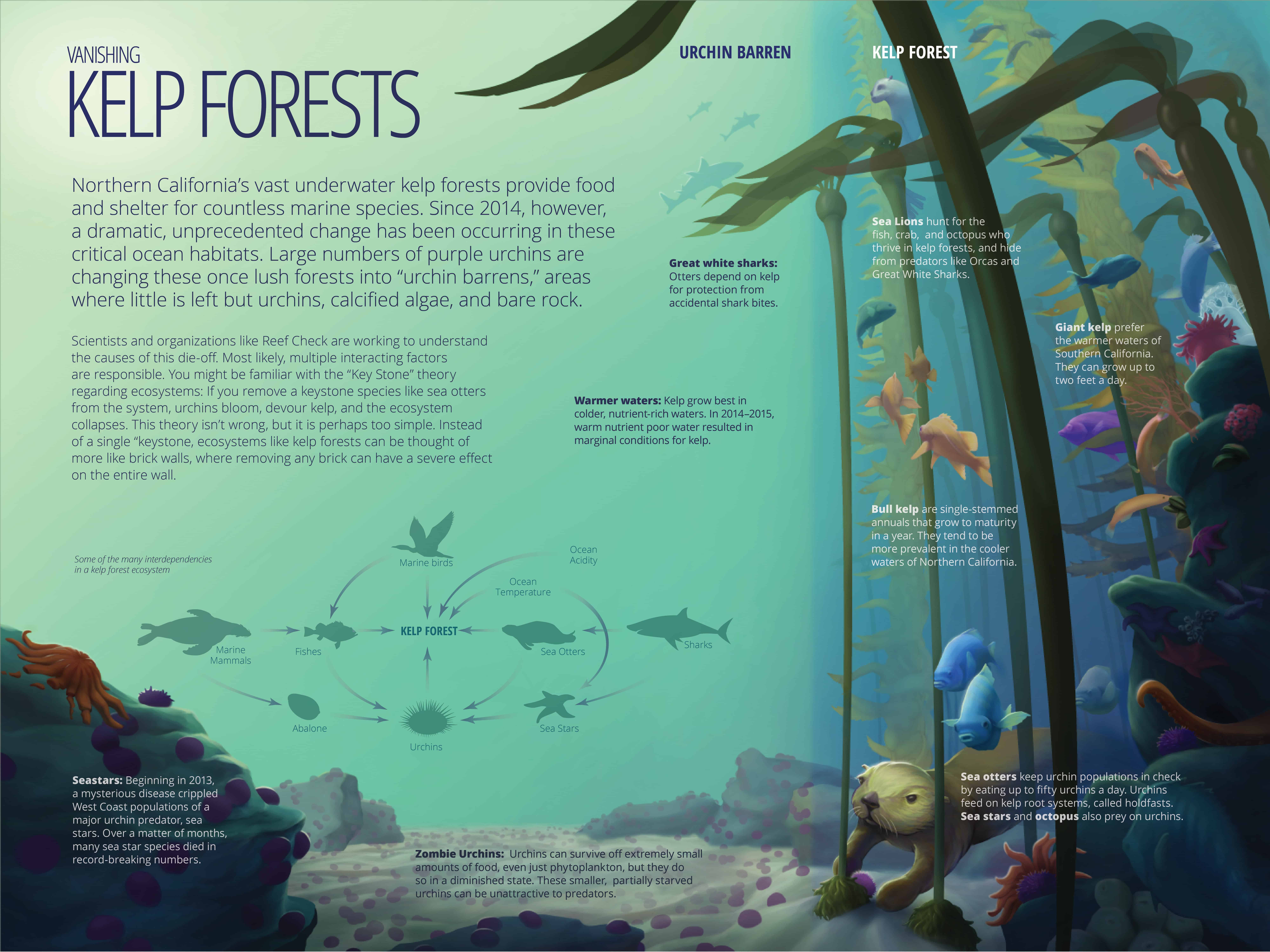
Kelp Forest Urchin Barren Dynamics Reef Check

How Does Energy Flow And Is Transferred Through An Ecosystem Ppt Download

What Would Be An Example Of A Food Chain In The Giant Kelp Forest Ecosystem Landmark Diner Nyc

Kelp Forest Science Lesson Plan Made By Teachers

Https Www Google Com Search Q Kelp Forest Kelp Forest Forest Ecosystem Forest

Kelp Forest Conservation Teacher Resources Aquarium Of The Pacific

Comments
Post a Comment